Have you ever wondered “Why Food Makes You Sleepy” feel like taking a nap after a big meal? It’s not just because you ate too much or because certain foods are heavy. There’s actual science behind why food makes us sleepy! Think about how you feel after eating a cheeseburger and fries or enjoying a Thanksgiving feast. That heavy, tired feeling is what some people call a “food coma.” In this article, we’ll explore why certain foods make us feel so lethargic.
After you eat, your body’s blood flow changes. It sends more blood to your stomach and intestines to help with digestion. This can make you feel tired because less blood is going to your brain. Also, a hormone called melatonin increases after eating, making you even sleepier.
Some foods contain an amino acid called tryptophan. When you eat these foods, your body turns tryptophan into hormones like serotonin and melatonin, which help you relax and feel sleepy. Foods like turkey, chicken, and cheese are high in tryptophan, so they can make you feel extra drowsy.
Carbohydrates, found in foods like bread and pasta, can also make you feel sleepy. They cause your blood sugar levels to rise and then fall quickly, which can leave you feeling tired. Eating a big meal can also raise your body temperature as it works to digest the food. Afterward, when your temperature drops back down, you might feel sleepy.
Even spicy foods can make you feel tired! They contain a substance called capsaicin, which can relax your brain and make you feel sleepy. Alcohol is another culprit. While it might make you feel sleepy at first, it can actually disrupt your sleep later in the night. Eating too close to bedtime or having large meals can also make you feel tired because your body is busy digesting when it should be resting.
In this article, we’ll give you some tips to avoid feeling sleepy after eating and explain why it’s important to get enough good-quality sleep. So, if you’ve ever wondered why food makes you feel so tired, keep reading to find out more!
In our previous discussion about the role of sleep in diet and a healthy lifestyle, we explored how quality sleep is essential for overall well-being. If you’re interested in learning more about how sleep impacts your dietary habits and overall health, you can read the full article here. Understanding this connection sheds light on why prioritizing both sleep and nutrition is crucial for maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Table of Contents
ToggleBlood Flow Changes After Eating
One of the reasons why food makes you sleepy is due to changes in blood flow after eating. When you begin digesting a meal, your body directs more blood to your stomach and intestines to help with the digestion process.
This diversion of blood from the brain to the digestive system can leave you feeling tired and sluggish. With less blood flowing to the brain, you may experience mental fatigue, lack of focus, and drowsiness. The sleep hormone melatonin also naturally increases after eating, which can amplify this effect.
Large meals require more digestion and thus pull more blood away from the brain, making you even sleepier. However, the effect is usually temporary. Once digestion is complete, blood flow returns to normal levels and food-induced tiredness subsides.
Foods High in Tryptophan

One of the reasons food can make you feel sleepy is due to the amino acid tryptophan. Tryptophan is found in many protein-rich foods and is a precursor for serotonin and melatonin, which are hormones that help regulate sleep cycles and promote feelings of relaxation and drowsiness.
When tryptophan enters the brain, it gets converted into serotonin. Serotonin levels naturally rise when it’s close to bedtime, signaling the body to prepare for sleep. Some of this serotonin gets converted into melatonin, a hormone that regulates your circadian rhythm. Higher melatonin levels make you feel sleepier.
Foods that are particularly high in tryptophan include:
- Turkey
- Chicken
- Tuna
- Eggs
- Cheese
- Soybeans
- Nuts
- Seeds
Eating these foods rich in tryptophan causes a spike in serotonin and melatonin production, which can make you feel drowsy and ready for bed. This is why many people feel sleepy after eating a big meal containing foods like turkey, which has particularly high levels of tryptophan.
Carbs Cause Insulin Release
Carbohydrates cause your blood sugar (glucose) levels to rise. This increase in blood sugar signals your pancreas to secrete insulin. Insulin is the hormone responsible for allowing glucose to leave the bloodstream and enter your cells to be used for energy.
When insulin removes glucose from your bloodstream, it can cause your blood sugar to drop suddenly. This swift decrease in blood sugar signals your brain that you need food, making you feel tired or sleepy.
High-carb foods like bread, rice, pasta, chips, sweets, and sodas digest quickly and cause blood sugar and insulin levels to spike and crash rapidly. This blood sugar rollercoaster can leave you feeling drowsy and lethargic.
Choosing slow-digesting carbs like whole grains, beans, lentils, and fruits can provide a steady supply of energy without the sleepy after-effects of high-glycemic foods.
Eating Raises Body Temperature
After eating a meal, your body has to work to digest the food. This digestion process requires energy and causes your body temperature to rise slightly. This rise in temperature activates your body’s cooling system. As your body temperature starts to drop back down after eating, this quick change in temperature makes you sleepy. The drop in body temperature signals your brain that it’s time to sleep.
Research has shown that body temperature rises by up to 1-2°F after eating, especially a heavy, carbohydrate-rich meal. Then as digestion is completed, body temperature begins to fall again and often drops below pre-meal levels. This temperature rollercoaster that happens after eating fatigues the body and leads to sleepiness.
Explore Spicy Food’s Phenomenon: Why Food Makes You Sleepy
Many people feel tired after eating spicy foods like hot peppers or curry dishes. The active component in spicy foods that creates the hot sensation is capsaicin. Capsaicin stimulates nerve fibers in the tongue, which send signals to the brain. This triggers a burning, painful feeling that our brains perceive as spicy.
Interestingly, research shows that capsaicin may also have a sedative effect on the brain. When neurons in the brain detect capsaicin, they start releasing sleep-promoting neurotransmitters like serotonin and endorphins. These calming brain chemicals can make you feel relaxed and sleepy after eating spicy foods.
Additionally, capsaicin may help induce sleep by increasing body temperature slightly, then causing a cooling, sleep-promoting effect afterward. So while spicy foods can sometimes feel stimulating, they can actually have a soothing, sleep-enhancing impact as well.
Alcohol Disrupts Sleep Cycles
Alcohol consumption before bedtime can significantly disrupt the normal sleep cycle and architecture. Even though alcohol may help you fall asleep faster initially, it reduces rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and fragments sleep during the second half of the night.
REM sleep is critical for memory consolidation and restorative sleep. When REM sleep is disrupted, you may experience less restful sleep and wake up exhausted the next morning.
Alcohol also blocks tryptophan conversion into melatonin and adenosine, which are hormones that promote sleep. This leads to sleep disturbances and disrupted circadian rhythms.
Research shows that drinking alcohol 4-6 hours before bedtime is associated with increased wakefulness in the second half of the night. This affects sleep quality and makes it difficult to fall back asleep.
Therefore, it’s best to avoid alcohol for at least 4 hours, and ideally 6-8 hours, before bedtime to prevent sleep disruptions and next-day drowsiness.
Eating Too Close to Bedtime

Eating too close to your bedtime can keep your body busy digesting when it should be winding down for rest. Going to sleep with a full stomach doesn’t allow enough time for your body to properly digest the food before laying down.
Ideally, you should finish eating dinner at least 2-3 hours before bed. This gives your body adequate time to digest and process the food before you try to fall asleep. Eating too soon before bed can cause indigestion, acid reflux, and poor sleep quality.
If you go to bed feeling overly full from a large meal, it can lead to tossing and turning throughout the night. Your body is expending energy trying to digest rather than relaxing into deep, restorative sleep. Heavy foods like fatty meats, creamy pasta dishes, or decadent desserts require the most time to fully digest.
Try to eat a light dinner, avoid heavy snacks before bedtime, and give yourself enough of a buffer before laying down. You’ll find you fall asleep faster and sleep more soundly when you don’t overload your stomach right before bed.
Big Meals Require More Digestion
When you eat a large meal, your body needs to direct more blood and energy to your stomach to properly break down all that food. This digestion process requires a lot of work, so your body activates your parasympathetic nervous system. This system is responsible for relaxation and digestion and it also makes you feel sleepy.
Eating a huge dinner leaves your body expending energy on digestion when that energy could have been used to keep you awake and alert. So after polishing off a big meal, it’s common to feel sluggish, sleepy, and ready for bed. Your body is simply too busy digesting to keep you fully energized.
To avoid food coma after a large dinner, try eating smaller meals spaced throughout the day. Your body can more effectively digest small amounts of food at a time. And beware of heavy, rich foods in large portions – these take the most energy to digest. Save your biggest meals for earlier in the day if possible.
Fatty Foods Slow Digestion
Foods that are high in fat content take a long time for your body to digest. This is because fats need to be broken down by bile acids and enzymes before they can be absorbed by the small intestine. High-fat foods like fast food, fatty cuts of meat, cheese, and desserts require more time for digestion compared to low-fat foods.
When you eat fatty foods, the digestive process draws more blood to your stomach and away from other parts of your body. The digestion of fats is also slower than carbs or protein. This combination makes you feel sluggish and sleepy after eating high-fat foods.
Fast food and processed snacks are common culprits for food coma. The high amount of fat causes digestion to slow down. This results in sleepiness and low energy levels after eating these fatty foods. To avoid food coma, limit high-fat foods close to bedtime or times when you need to be awake and alert.
Avoiding Food Coma
There are simple strategies you can use to avoid feeling overly tired and sluggish after eating. Here are some tips:
Eat smaller meals: Don’t overload your digestive system by eating large portions. Spread your food intake out over 5-6 smaller meals throughout the day.
Have an earlier dinner: Eat dinner at least 2-3 hours before bedtime so your body has time to digest. This prevents digestive issues from disrupting your sleep.
Choose low-carb meals: Starchy carbs like pasta, bread, and potatoes cause bigger blood sugar spikes and crashes. Focus on lean protein, vegetables, and healthy fats.
Avoid alcohol: Alcohol can make you fall asleep faster but leads to poor quality sleep later in the night as the alcohol wears off. Skip the alcohol with dinner or late at night.
Making simple adjustments to your eating habits can go a long way towards avoiding that overloaded, sluggish feeling after meals. You’ll sleep better and wake up feeling more refreshed.
When to See a Doctor
If feeling sleepy after eating begins impacting your daily life, it’s important to see your doctor. Excessive daytime sleepiness that interferes with normal activities is a red flag for an underlying health condition.
Your doctor can help determine if there’s an identifiable cause, such as:
- Sleep apnea
- Narcolepsy
- Thyroid disorders
- Anemia
- Depression
- Medication side effects
- Other medical conditions
After ruling out any medical reasons, your doctor may recommend lifestyle changes, sleep hygiene tips, or cognitive behavioral therapy to improve sleep habits. If the excessive sleepiness persists and cannot be explained, they may recommend a sleep study.
The earlier you seek help for significant fatigue or sleepiness, the sooner any health issues can be identified and treated. Ignoring the problem rarely makes it go away. So be sure to talk to your doctor if feeling abnormally sleepy on a regular basis.
Health Risks of Poor Sleep
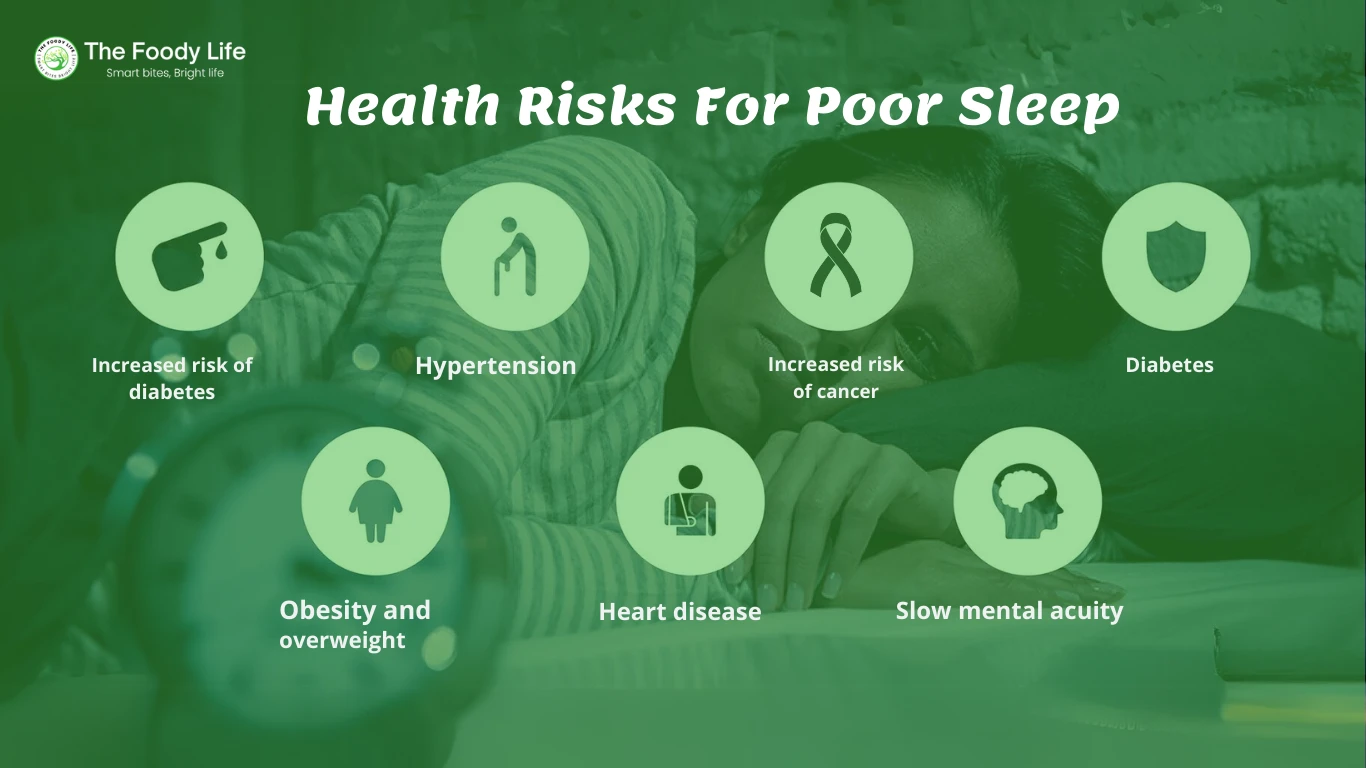
Getting inadequate sleep can have significant negative effects on your health in the long run. Some of the most notable risks include:
Obesity: Lack of sleep affects hormones that regulate hunger and appetite, specifically increasing levels of ghrelin which stimulates appetite, and decreasing levels of leptin which suppresses appetite. This can lead to overeating and weight gain over time.
Heart disease: Insufficient sleep increases inflammation which damages blood vessels and leads to atherosclerosis. It also raises blood pressure and disrupts metabolism, increasing the risk of heart disease.
Diabetes: Poor sleep affects insulin sensitivity and impairs glucose metabolism which are risk factors for developing type 2 diabetes.
Hypertension: Sleep deprivation activates the sympathetic nervous system which raises blood pressure. Over time, chronic lack of sleep significantly increases the risk of hypertension.
Tips for Better Sleep
Getting enough high-quality sleep is essential for good health. Here are some tips to help you get the rest you need:
Set a Consistent Sleep Schedule
Going to bed and waking up at the same time each day trains your body’s internal clock for better sleep. Try to stick to your schedule, even on weekends.
Limit Screen Time Before Bed
The blue light from phones, tablets, and TVs can suppress melatonin and make it harder to fall asleep. Avoid screens in the hour before bedtime.
Get Regular Exercise
Physical activity during the day can help you fall asleep faster at night. However, exercising too close to bedtime may have the opposite effect.
Eat a Sleep Friendly Diet
Avoid heavy meals, spicy foods, caffeine, and alcohol before bed, as these can disrupt sleep. Light snacks like turkey, nuts, and tart cherry juice can help induce sleep.
Optimize Your Sleep Environment
Keep your room cool, dark, and quiet for better sleep. Consider using blackout curtains, a white noise machine, earplugs, or an eye mask if needed.
Conclusion
There are several surprising reasons why food can make you sleepy. Eating causes changes in blood flow, spikes in insulin, raises body temperature, and requires the body to expend energy digesting. Foods high in carbohydrates, fat, protein, and calories are the biggest culprits for food-induced sleepiness. Alcohol also disrupts normal sleep cycles. Eating too close to bedtime or overeating can make you sleepy as your body diverts resources to digestion. While occasional food coma is not harmful, chronic poor sleep can have negative health impacts. Being mindful of how certain foods affect your energy levels, avoiding heavy meals before bed, staying hydrated, and developing good sleep habits can help minimize drowsiness after eating.
In summary, food-induced sleepiness is a complex phenomenon, but understanding the underlying mechanisms can empower you to make dietary choices that optimize your energy levels and alertness throughout the day. Paying attention to timing and portions and limiting sluggishness-promoting foods and beverages may help you avoid that after meal sleepy feeling.









42 thoughts on “The Surprising Reasons Why Food Makes You Sleepy?”
Pingback: A Guide: what foods to avoid if alkaline phosphatase is high
I’ve been following this blog for years and it’s amazing to see how much it has grown and evolved Congratulations on all your success!
Your writing is a breath of fresh air It’s clear that you put a lot of thought and effort into each and every post
Your positive and uplifting words are like a ray of sunshine on a cloudy day Thank you for spreading light and positivity in the world
I appreciate how this blog promotes self-growth and personal development It’s important to continuously strive to become the best version of ourselves
itaque dolorem natus occaecati vero voluptatem consectetur impedit maxime ex harum qui dolorem ad. quisquam ut possimus culpa eligendi omnis molestiae aut neque quidem consequatur voluptatem placeat a
oi, gostei muito da sua escrita, compartilhe, entraremos em contato mais sobre seu artigo na AOL, preciso de um especialista nesta área para resolver meu problema Talvez seja você. Ansioso para vê-lo
Vitazen Keto Gummies I do not even understand how I ended up here, but I assumed this publish used to be great
Hi i think that i saw you visited my web site thus i came to Return the favore Im attempting to find things to enhance my siteI suppose its ok to use a few of your ideas
What i do not understood is in truth how you are not actually a lot more smartlyliked than you may be now You are very intelligent You realize therefore significantly in the case of this topic produced me individually imagine it from numerous numerous angles Its like men and women dont seem to be fascinated until it is one thing to do with Woman gaga Your own stuffs nice All the time care for it up
SocialMediaGirls Hi there to all, for the reason that I am genuinely keen of reading this website’s post to be updated on a regular basis. It carries pleasant stuff.
Insanont I really like reading through a post that can make men and women think. Also, thank you for allowing me to comment!
The posts inspire me regularly. The depth you bring to The topics is truly exceptional.
Handling topics with grace and authority, like a professor, but without the monotone lectures.
The post was a beacon of knowledge. Thanks for casting light on this subject for me.
The voice shines through The writing like a beacon, guiding us through the darkness of ignorance.
Jinx Manga There is definately a lot to find out about this subject. I like all the points you made
The perspective is like a rare gem, valuable and unique in the vastness of the internet.
The thoughtful analysis has really made me think, in a way that’s as stimulating as a deep gaze into The eyes.
The grace and authority you handle topics with are as mesmerizing as a moonlit dance. I’m thoroughly impressed.
Clochant very informative articles or reviews at this time.
Bookmarking this! The practical advice is something I’ll definitely be coming back to.
You have a knack for presenting hard to understand topics in an engaging way. Kudos to you!
Its wonderful as your other blog posts : D, regards for putting up.
I’m so grateful for the information you’ve shared. It’s been incredibly enlightening!
The Writing is a constant source of inspiration and knowledge. Thank you!
Blue Techker This was beautiful Admin. Thank you for your reflections.
certainly like your website however you have to take a look at the spelling on quite a few of your posts. Many of them are rife with spelling problems and I find it very troublesome to tell the reality then again I will definitely come back again.
The post has broadened my perspective in ways I didn’t expect. Thank you for that.
The dedication to high quality content is evident. Keep up the great work!
Engaging with The Writing is like savoring a gourmet meal; every bite (or word) is to be enjoyed.
Provoked thought and taught me something new, as if my brain needed more exercise.
The voice shines through The writing like a beacon, guiding us through the darkness of ignorance.
This article was a delightful read. The passion is clearly visible!
I’m so grateful for the information you’ve shared. It’s been incredibly enlightening!
The writing style is like a signature scent—distinct, memorable, and always pleasant.
This is one of the most comprehensive articles I’ve read on this topic. Kudos!
The insights are like a fine wine—rich, fulfilling, and leaving me wanting more.
It is the best time to make a few plans for the future and it is time to be happy. I have read this submit and if I could I wish to counsel you some fascinating issues or suggestions. Maybe you can write subsequent articles referring to this article. I desire to learn more issues approximately it!
Provoked thought and taught me something new, as if my brain needed more exercise.
What a refreshing take on this subject. I completely agree with The points!
Thank you for any other great article. The place else could anyone get that type of information in such a perfect manner of writing? I’ve a presentation next week, and I am on the look for such information.